
A genotyping test determines differences in an ind...
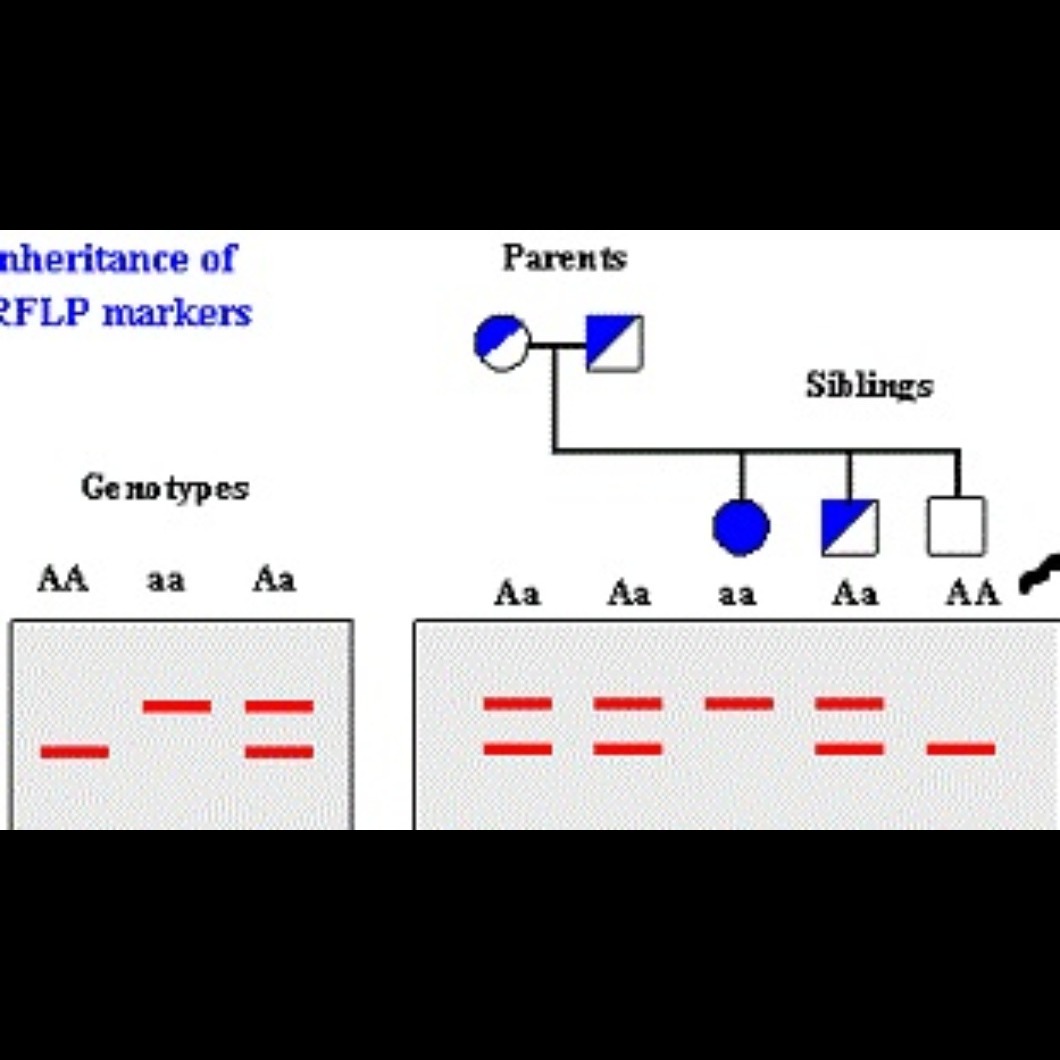
A genotyping test determines differences in an individual's genetic makeup by examining their DNA sequence and comparing it to other samples or reference sequences. It identifies variations like single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) or other genetic differences. Genotyping is used in various fields including disease diagnosis, population studies, and forensic science. Key aspects of genotyping tests: Purpose: To identify genetic variations within an individual or between individuals. Methods: Several techniques are used, including DNA sequencing, mass spectrometry, molecular beacons, SNP microarrays, and PCR-based methods. Applications: Clinical: Identifying genetic predispositions to diseases, predicting drug responses, and diagnosing infections. Research: Understanding population genetics, evolution, and disease mechanisms. Forensic: Identifying individuals based on DNA fingerprints. Examples: HCV Genotyping: Identifies the specific genetic variation of the Hepatitis C virus to help understand its transmission and treatment. Clopidogrel Genotyping: Determines if an individual may be less responsive to the antiplatelet drug clopidogrel. CYP2C19 Genotyping: Identifies individuals who may have altered CYP2C19 enzyme activity, potentially affecting their response to certain medications. SNP Genotyping: Focuses on single nucleotide polymorphisms, which are common genetic variations. In Pimpri Chinchwad Pune Exploring Truth... NIDAN Pathology Laboratory ISO 9001:2015 Certified Book Free Home Collection : 7775837228/8999989854 Email Id: nidanpathology331@gmail.com Rupeenagar Chakan | Punawale Wakad | Pimpari | Krushnanagar | Ravet
Subscribe for latest offers & updates
We hate spam too.


